https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42840?language=python3
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
다들 코딩테스트를 하시기에 문제 풀기 좋아하는 나도 참여해보았다.
원래는 파이썬 강의를 심화까지 다 들은 뒤 도전하려 했으나,
강의가 머리에 잘 들어오지 않아 오후에는 코딩테스트를 하였다!
✅ 일단 입출력 예 #1로 출력되게 해보기
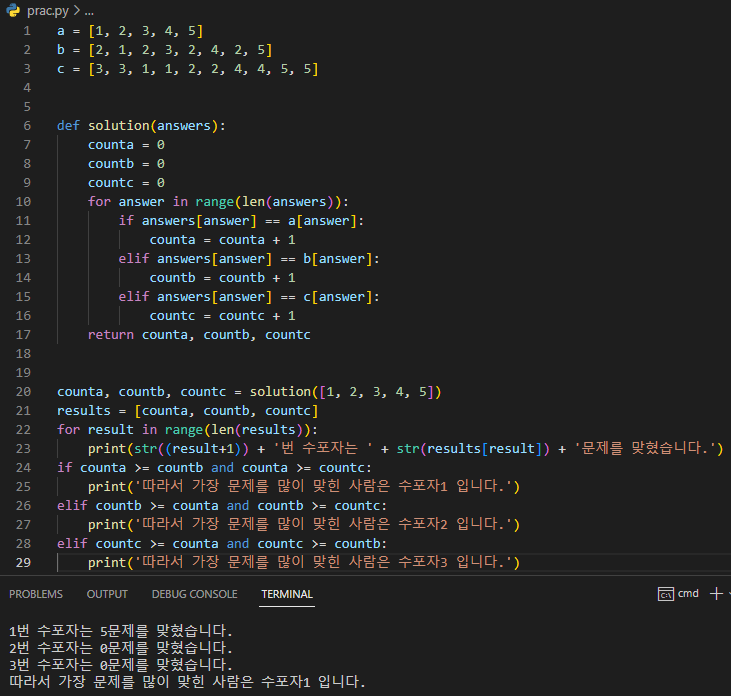
처음에 23번째 줄 print에서 TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'str' 가 떠서
str()을 추가하니 잘 나오게 되었다.
자바에서는 숫자와 문자를 합쳐 출력하면 그냥 문자로 출력되지만
파이썬에서는 숫자 앞에 str(값)을 붙여 문자로 만들거나 int(값)을 붙여 숫자로 만들어 줘야 함
solution.py 중간 상황:
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
b = [2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 2, 5]
c = [3, 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 5, 5]
def solution(answers):
counta = 0
countb = 0
countc = 0
for answer in range(len(answers)):
if answers[answer] == a[answer]:
counta = counta + 1
elif answers[answer] == b[answer]:
countb = countb + 1
elif answers[answer] == c[answer]:
countc = countc + 1
return counta, countb, countc
counta, countb, countc = solution([1, 3, 2, 4, 2])
results = [counta, countb, countc]
for result in range(len(results)):
print(str((result+1)) + '번 수포자는 ' + str(results[result]) + '문제를 맞혔습니다.')
if counta >= countb and counta >= countc:
print('따라서 가장 문제를 많이 맞힌 사람은 수포자1 입니다.')
elif countb >= counta and countb >= countc:
print('따라서 가장 문제를 많이 맞힌 사람은 수포자2 입니다.')
elif countc >= counta and countc >= countb:
print('따라서 가장 문제를 많이 맞힌 사람은 수포자3 입니다.')
✅ 시험 문제가 많아질 경우
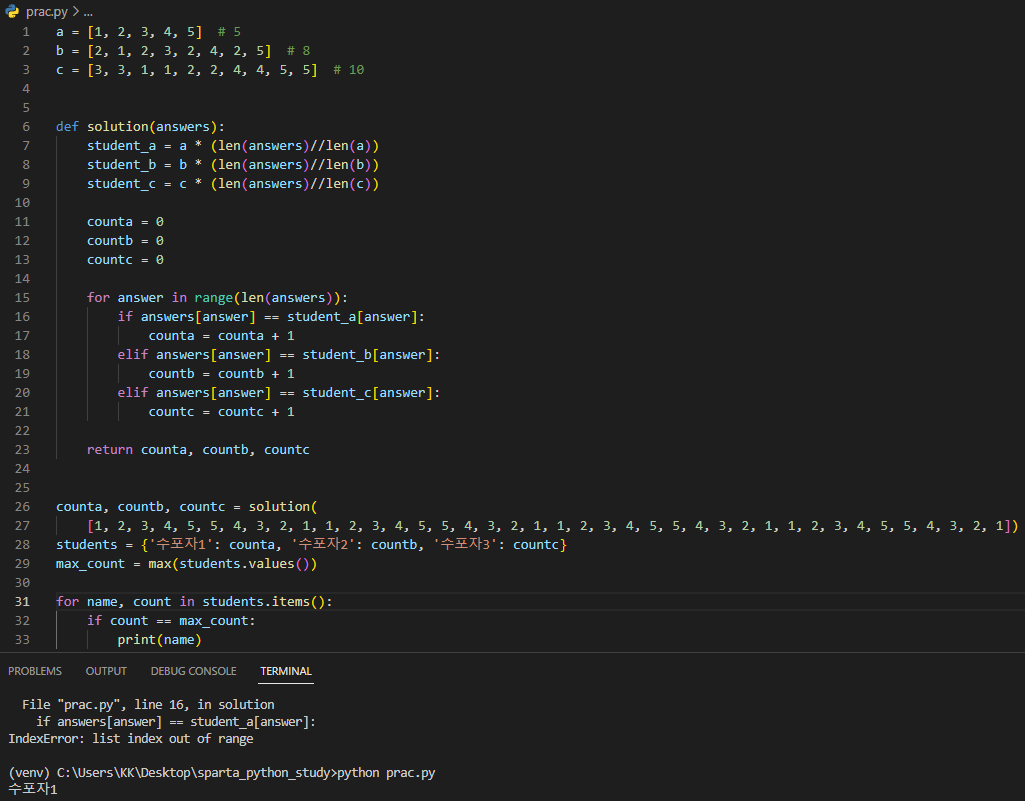
a, b, c의 리스트가 각 5, 8, 10개라서
answers에 40개의 값이 담긴 리스트를 넣으니 괜찮은데 다른 개수로 넣으면,
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "prac.py", line 26, in <module>
counta, countb, countc = solution(
File "prac.py", line 16, in solution
if answers[answer] == student_a[answer]:
IndexError: list index out of range
이런 에러가 뜬다.
student_a = a * (len(answers)//len(a)+1)
student_b = b * (len(answers)//len(b)+1)
student_c = c * (len(answers)//len(c)+1)
아까 곱한 몫에서 +1씩만 더해 곱해줘도 student_a,b,c의 길이가 answers 보다 길어지게 되므로 ok
for i in range(len(answers)):
이 부분에서는 enumerate()를 활용하면 좋다고 한다!
✅ 더 간단하게
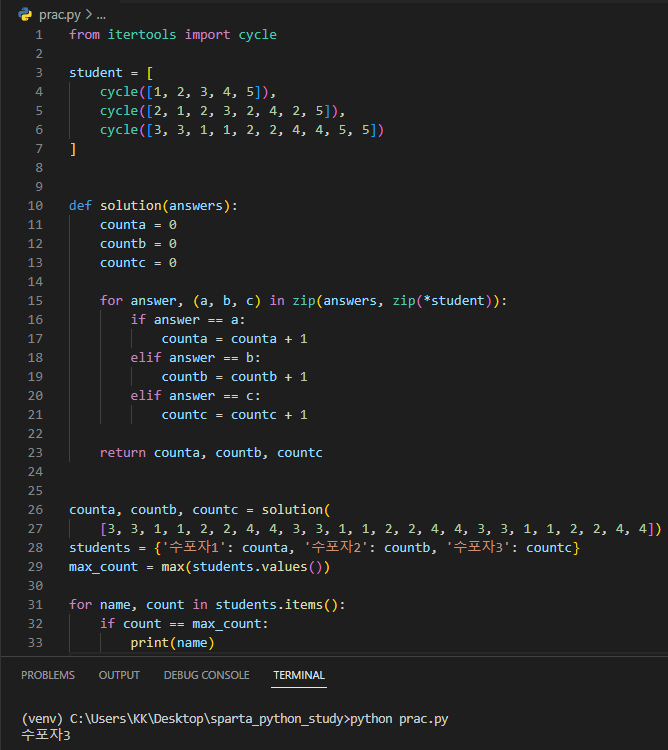
itertools의 cycle()
원하는 수만큼 list 반복 가능 👉 from itertools import cycle 필요
zip() 함수
여러개의 list를 하나로 묶음 👉 길이가 짧은 리스트에 맞춰짐
list로 dictionary 만들기 가능
zip(*student) : 패킹(packing)
오늘 배운 패킹 👉 list나 dictionary를 함수에 입력할 때 주로 사용
26번째 줄이 마음에 안 듦..
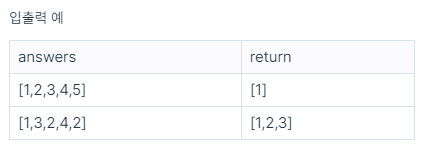
[입출력 예]를 보면, 맞힌 문제가 없을 경우 출력이 안 되고,
맞힌 문제가 있다면 맞힌 수만큼 차례대로 출력되어야 한다.
✅ 못 맞추면 출력X, 맞힌 수만큼 정렬
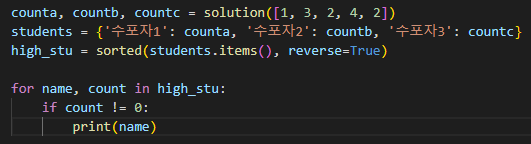
sorted(students.items(), reverse=True) 로 내림차순 정렬을 했는데
처음에 딕셔너리의 밸류값을 가져오려고 students.values()를 하니
Traceback (most recent call last): File "prac.py", line 30, in <module> for name, count in high_stu: TypeError: cannot unpack non-iterable int object
high_stu는 반복 가능한 객체가 아니라 언패킹할 수 없다는 오류
패킹 때문에 오류가 떠서 students.items()로 변경!
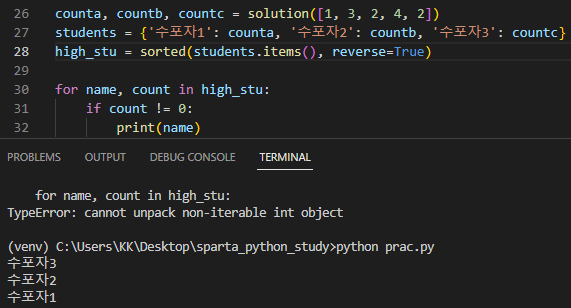
👆 students = {'수포자1': 2, '수포자2': 2, '수포자3': 1} 이건데 수포자 3 2 1 로 뜸ㅠ
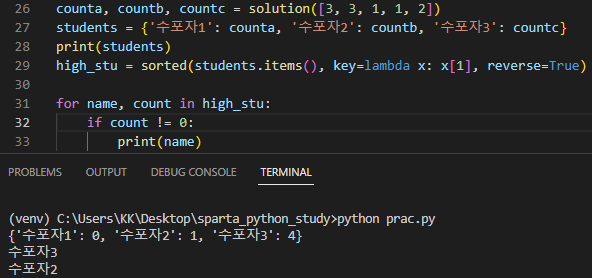
sorted에 key=lambda x: x[1]을 입력해주니 잘 뜬다^_^
👉 각 항목의 두번째 요소('count')를 사용하여 정렬하기 위한 것!
분명 map, filter, lambda 이런 게 있구나만 알면 된다고 하셨는데..
파이썬 문법 기초 복습할 때 다시 잘 봐야지~!
solution.py:
from itertools import cycle
student = [
cycle([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]),
cycle([2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 2, 5]),
cycle([3, 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 5, 5])
]
def solution(answers):
counta = 0
countb = 0
countc = 0
for answer, (a, b, c) in zip(answers, zip(*student)):
if answer == a:
counta = counta + 1
elif answer == b:
countb = countb + 1
elif answer == c:
countc = countc + 1
return counta, countb, countc
counta, countb, countc = solution([3, 3, 1, 1, 2])
students = {'수포자1': counta, '수포자2': countb, '수포자3': countc}
print(students)
high_stu = sorted(students.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for name, count in high_stu:
if count != 0:
print(name)
'코딩테스트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 코딩테스트 입문_최빈값 구하기_sorted() (0) | 2023.03.30 |
|---|---|
| 코딩테스트 입문_분수의 덧셈_fractions 모듈 (2) | 2023.03.24 |
| 코딩테스트 카카오_숫자 문자열과 영단어_isdecimal replace (0) | 2023.03.24 |
| 코딩테스트 입문_옹알이(1)_permutations (2) | 2023.03.23 |
| 코딩테스트 연습문제_짝수와 홀수 (0) | 2023.03.22 |